The human body is a complex system, and one of its most fascinating relationships is the connection between the gut and the brain. This relationship, often called the gut-brain axis, is a two-way communication system that influences our overall health, including our cognitive functions such as memory, mood, and mental clarity.
At the heart of this connection is the gut microbiome, a vibrant community of trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi living in our digestive tract. While the gut microbiome is best known for helping with digestion, its influence goes much further:
- Neurotransmitter Production: The gut microbiome helps produce essential neurotransmitters, like serotonin and dopamine, which regulate our emotions and cognitive functions.
- Mood and Mental Health: A healthy gut can improve mood and reduce stress by ensuring a steady flow of these neurotransmitters.
- Mental Clarity: A balanced gut can sharpen focus and memory by supporting the production of brain-boosting chemicals.
By taking care of your gut, you can also enhance your mental and emotional well-being. Improving gut health is not just about digestion—it’s about optimizing how your brain works too.
The Gut’s Role in Brain Health
One of the gut’s most remarkable features is its ability to produce neurotransmitters, essential chemical messengers affecting our mood, cognition, and overall mental health. Key neurotransmitters such as serotonin, GABA, and dopamine are produced or influenced by gut bacteria, demonstrating the gut’s pivotal role in brain function.
- Serotonin: Known as the “feel-good” hormone, serotonin regulates mood, emotions, and feelings of well-being. Surprisingly, about 95% of the body’s serotonin is produced in the gut! A balanced gut microbiome supports consistent serotonin production, which in turn helps maintain emotional stability and a positive mood.
- GABA: Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is another neurotransmitter produced in the gut, and it plays a critical role in calming the brain and reducing anxiety. When the gut is healthy, GABA production is optimized, promoting relaxation and helping to ease mental stress.
- Dopamine: Often referred to as the “motivation” neurotransmitter, dopamine influences focus, drive, and reward-motivated behavior. Gut bacteria play a role in maintaining steady dopamine levels, meaning an imbalanced gut can lead to difficulties with concentration and motivation, commonly known as brain fog. Supporting a healthy gut microbiome can enhance mental clarity and cognitive function.
In addition to neurotransmitter production, the gut also communicates with the brain via the vagus nerve. This nerve acts as a direct communication line, sending signals between gut neurons and the brain. Through the vagus nerve, the gut can influence hunger, cravings, and even emotional responses to food, highlighting the deep connection between what we eat and how we feel mentally.
Dietary Strategies to Support Gut and Brain Health
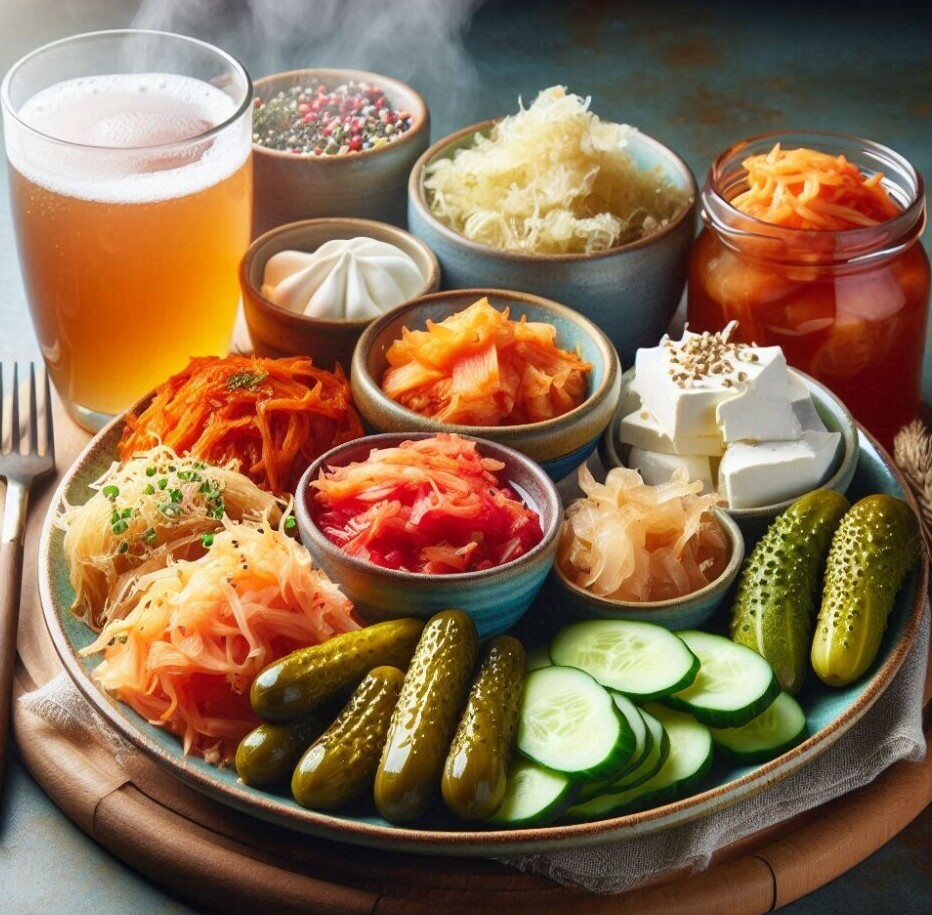

Maintaining a healthy gut is key to optimizing brain function, and diet plays a central role in achieving this balance. Here are some dietary strategies to nourish both the gut and the brain:
- Incorporate Fermented Foods: Fermented foods such as kimchi, sauerkraut, kefir, and yogurt are rich in probiotics—beneficial bacteria that boost gut health. These foods help increase microbial diversity in the gut, reducing inflammation and promoting better cognitive function. Aim for 4-6 servings of fermented foods daily, particularly low-sugar options, to support mental and emotional health.
- Embrace Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber is essential for gut health, as it supports the production of beneficial neurotransmitters. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are excellent sources of fiber that promote regular digestion and a healthy gut microbiome. Even though fiber doesn’t directly increase the diversity of gut bacteria, it supports overall digestive health, indirectly positively affecting brain function.
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: Probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria to the gut, while prebiotics—found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas—fuel these bacteria. Incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into your diet can improve cognitive performance by balancing neurotransmitter levels and reducing inflammation, ultimately supporting brain health.
- Avoid Artificial Sweeteners: Research has shown that artificial sweeteners can disrupt the gut microbiome, negatively impacting brain function. Opt for natural alternatives such as stevia or monk fruit to protect your gut health and keep your brain sharp.
Early Life Gut Health and Long-Term Cognitive Benefits
The gut-brain connection starts early in life, and establishing a healthy gut microbiome during childhood can have long-lasting effects on cognitive and emotional development. Here are some key strategies for promoting gut health in children, which can set the stage for improved brain function throughout life:
- Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding is one of the most effective ways to promote a healthy gut microbiome in infants. Breast milk provides essential nutrients and beneficial bacteria that help develop a diverse and robust gut flora. In addition to its nutritional benefits, breastfeeding has been linked to improved immune function and cognitive health.
- Exposure to Diverse Environments: Allowing children to play outside, interact with pets, and experience different natural environments can introduce a range of microbes that enrich their gut flora. This microbial diversity is crucial for mental resilience and cognitive ability, helping children develop the tools they need for emotional and intellectual growth.
- Judicious Use of Antibiotics: While antibiotics are sometimes necessary, their overuse can harm the gut microbiome by wiping out beneficial bacteria. This can have long-term effects on cognitive and emotional health. Use antibiotics only when absolutely necessary to protect the integrity of the gut microbiome and ensure healthy brain development.
Even for adults, it’s never too late to focus on gut health. Eating various foods, reducing stress, and improving sleep habits can boost your gut microbiome, leading to better cognitive function and enhanced emotional well-being.
Summary of Research on Gut Microbiota and Cognitive Function
Numerous recent studies have highlighted the powerful connection between gut microbiota and cognitive performance. Researchers have found that a diverse and balanced gut microbiome can significantly affect brain health, particularly in high-stress environments.
- Cognitive Flexibility and Executive Function: Studies have shown that individuals with a more diverse gut microbiome tend to have better cognitive flexibility and executive function. This means they are more capable of adapting to new situations and solving complex problems.
- Memory and Attention: Several intervention studies have demonstrated that manipulating the gut microbiome—often through probiotics—can improve memory and attention span. In one review of 12 studies, 11 found positive results linking gut health to better cognitive performance.
While the current body of research is promising, it represents only the beginning of our understanding of the gut-brain axis. As more studies explore the intricate relationship between gut health and cognitive function, we will gain further insights into harnessing this connection to improve mental clarity, emotional resilience, and overall well-being.
Conclusion:
The relationship between gut health and brain function is more than an academic topic—it has practical implications for daily life. Focusing on gut health through diet and lifestyle choices can improve mental clarity, emotional stability, and overall cognitive function.
Whether incorporating more fermented foods into your diet, managing stress levels, or fostering a diverse microbiome in early life, taking care of your gut is one of the best ways to support a healthy, thriving brain.

This is a fascinating post! I had no idea that so much of our mental clarity and emotional well-being is tied to the health of our gut. It’s incredible to think that neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine are influenced by what we eat. I’m curious, what are your thoughts on how quickly someone might notice improvements in their mental clarity or mood after making changes to their diet, like incorporating more fermented foods? Also, how significant is the impact of artificial sweeteners on gut health?
Hey! Hanna,
Thanks for your comment!
It’s amazing how connected our gut is to mental clarity and mood. Many people notice improvements fairly quickly after adding more fermented foods—sometimes within a few weeks. Artificial sweeteners can negatively impact gut health by disrupting the balance of gut bacteria. I’ve written a blog post about it if you’d like to learn more
Do Artificial Sweeteners Destroy Your Gut Bacteria? – Get Healthy Gut
It’s really interesting how much we’re discovering about the link between gut health and brain function. A lot of health experts have shared amazing stories about patients who noticed better mental clarity, mood, and focus after paying attention to their microbiome. For instance, Dr. Michael Ruscio, a specialist in gut health, often mentions that balancing gut bacteria can help clear up brain fog and even assist with issues like anxiety and depression. Nutritionists are also highlighting the benefits of fermented foods, fiber-rich diets, and probiotics for both gut and brain wellness.
From my own experience, I’ve found that adding more prebiotics and probiotics to my meals, especially with foods like sauerkraut and kefir, has really boosted my focus and reduced mental fatigue. It seems like many others are feeling the same way, which really shows how interconnected our gut and brain are.
Have you noticed any changes in your mental state after tweaking your diet to focus on gut health? I’d love to hear about your experiences!
Hi Charzania
Thank you for sharing such thoughtful insights! I completely agree—it’s amazing how the gut-brain connection is gaining recognition, and experts like Dr. Ruscio have been instrumental in highlighting this link. Incorporating prebiotics and probiotics, as you mentioned with sauerkraut and kefir, can indeed have a noticeable impact on mental clarity and mood. Personally, I’ve noticed a more balanced energy and better focus since paying attention to my gut health, especially by adding more fermented foods and fiber-rich meals. It’s great to hear that others are experiencing similar benefits!