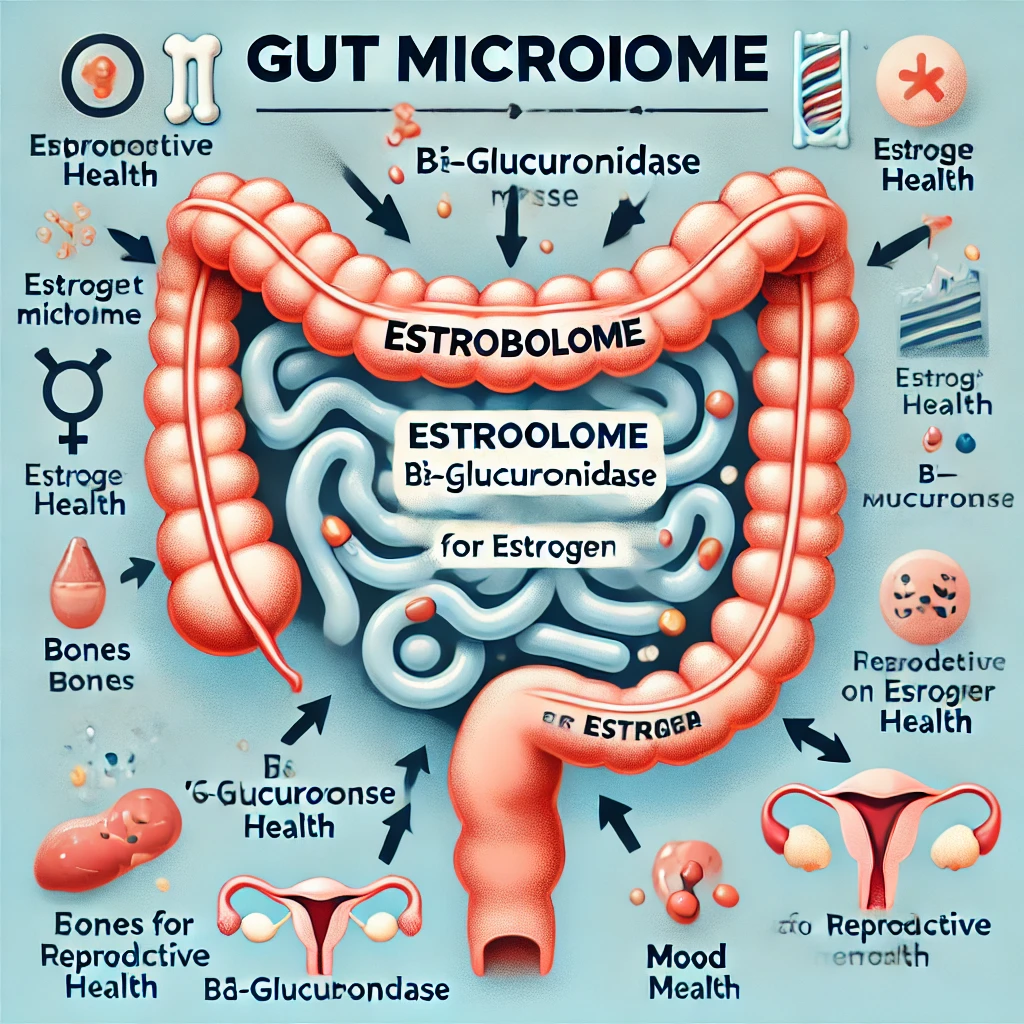
Your gut and hormones are in constant conversation, playing a major role in everything from mood and metabolism to bone health and cognitive function. This connection goes beyond just digestion. The gut microbiome, especially a specific group of bacteria called the estrobolome, is essential for regulating estrogen—a hormone crucial to overall health, particularly for women. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of gut and hormone health and discover practical ways to keep this vital connection balanced.
The Estrobolome: Your Gut’s Estrogen-Regulating Powerhouse
What Is the Estrobolome?
The estrobolome is a unique subset of the gut microbiome, consisting of bacteria that specifically metabolize estrogens. These bacteria produce an enzyme called β-glucuronidase, which helps break down estrogen in a way that allows it to be reabsorbed into the bloodstream. This “estrogen recycling” process is vital for maintaining balanced hormone levels in the body, impacting various health aspects.
How β-glucuronidase Supports Estrogen Balance
The enzyme β-glucuronidase enables the body to reabsorb estrogen, playing a role in regulating the amount of estrogen that stays active in the bloodstream. When the estrobolome is functioning well, it helps maintain balanced estrogen levels, supporting mood stability, metabolism, and even cardiovascular health.
Why Estrogen Balance Matters
For women, especially those in or post-menopause, estrogen plays a significant role in bone density, cognitive health, and heart health. Low estrogen levels, which often occur naturally with age, can impact these areas negatively. By promoting a balanced estrobolome, you can potentially support healthier estrogen levels, benefiting your overall wellness.
When Gut Imbalance Disrupts Hormones
What is Dysbiosis?
Dysbiosis occurs when there’s an imbalance in the gut bacteria, often caused by poor diet, stress, antibiotic use, or lack of dietary fiber. When dysbiosis affects the estrobolome, it can lead to hormonal chaos, particularly with estrogen levels.
Hormonal Chaos from Dysbiosis
An imbalanced gut can lead to either an excess or a deficiency in β-glucuronidase production. This can result in too much or too little estrogen in circulation:
- High Estrogen Levels: When certain bacteria overproduce β-glucuronidase, it can lead to elevated estrogen levels, which have been linked to mood swings, weight gain, and even an increased risk of certain cancers.
- Low Estrogen Levels: On the other hand, if there’s not enough β-glucuronidase-producing bacteria, estrogen levels may drop, leading to issues like fatigue, brain fog, and, in post-menopausal women, a heightened risk of osteoporosis.
Health Implications of Hormonal Imbalance
Imbalanced estrogen can affect women’s health in several ways. Higher levels are associated with a greater risk of breast and ovarian cancers, while lower levels can lead to symptoms like mood instability, low energy, and bone fragility. Keeping the estrobolome in balance helps mitigate these risks.
Supporting a Healthy Estrobolome for Hormonal Balance
Dietary Choices for a Strong Estrobolome
Promoting a healthy estrobolome begins with the right diet:
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, help nourish beneficial gut bacteria, promoting a diverse microbiome that supports the estrobolome.
- Fermented Foods: Incorporating fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kefir introduces beneficial probiotics to your system, supporting microbial diversity.
- Prebiotic Foods: Foods like garlic, onions, asparagus, and bananas contain prebiotics, which feed beneficial bacteria in the gut, encouraging a thriving microbiome.
Lifestyle Tips for a Balanced Gut
Aside from diet, lifestyle choices play an essential role in gut health:
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports digestion and ensures that nutrients reach the gut efficiently.
- Reduce Processed Foods: Processed foods often disrupt gut balance. Reducing these and focusing on whole, natural foods can benefit your gut and hormone health.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress has a negative impact on gut health, potentially leading to dysbiosis. Incorporating relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and regular exercise helps keep both your gut and hormones balanced.
Consider Probiotics and Fiber Supplements
While dietary changes are the foundation, some individuals may benefit from targeted probiotics and fiber supplements. Probiotics can support the microbiome, while fiber supplements provide the necessary fuel for beneficial bacteria. It’s wise to consult a healthcare provider to find the right supplement.
The Future of Gut and Hormone Health
Current Findings on the Gut-Hormone Link
Recent research reveals a compelling link between gut health and hormonal balance, particularly with estrogen. Studies suggest that fostering a healthy gut microbiome can help regulate estrogen levels, impacting everything from mood and metabolism to bone health. For post-menopausal women, this regulation may reduce risks associated with low estrogen, such as osteoporosis.
Exploring Potential Therapeutic Approaches
As we learn more, scientists are investigating how gut microbiome adjustments might one day help manage hormone-related conditions, such as menopausal symptoms and hormone-sensitive cancers. By focusing on gut health, we could be on the path toward new, non-invasive therapies for these conditions.
The Role of Personalized Nutrition
Some researchers are exploring how personalized nutrition can support the estrobolome and, in turn, hormonal health. By understanding an individual’s microbiome makeup, doctors may one day offer tailored dietary advice that optimizes hormonal balance through gut health.
Practical Tips for Gut and Hormone Harmony
Achieving a balanced gut microbiome doesn’t require an overhaul of your life. Here are some simple, actionable tips:
- Eat a Variety of Plant-Based Foods: A diverse range of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the fiber necessary for a healthy microbiome.
- Incorporate Fermented Foods Daily: Add foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi to your diet to introduce beneficial bacteria.
- Limit Sugar and Processed Foods: Processed foods can disrupt the gut microbiome, so focus on whole, natural foods.
- Consider Periodic Probiotic Use: After antibiotics or when you feel your digestion is off, a probiotic may help restore balance.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise supports digestive health, promoting microbial diversity in the gut.
- Monitor Your Mental Health: Prioritize stress-reduction practices like meditation or even regular time outdoors to support your gut and hormonal health.
Conclusion
The connection between gut health and hormones like estrogen is undeniable. The estrobolome plays a vital role in maintaining a balanced hormone system, which influences nearly every part of our well-being. A diet high in fiber and fermented foods, coupled with lifestyle habits like hydration and stress management, can go a long way in fostering a healthy estrobolome.
Taking proactive steps to support your gut health doesn’t just benefit digestion; it’s also crucial for your hormones, mood, energy levels, and long-term wellness. Stay informed as research advances, and remember that nurturing your gut is a powerful step toward achieving balanced hormones and optimal health.