What’s Diverticulosis?
Let’s start by defining a few terminologies diverticulosis is a sac or pouch formed in the colon. It occurs in the large intestines when constipation creates too much pressure while straining.
The colon becomes weak, and as a result, the walls of the intestines bulge out and form sacs.
Diverticulitis- This is when diverticulosis becomes inflamed. Due to irritation from stool, bacteria or food particles get stuck in the diverticula.
Diverticular disease- This is a full-blown disease. Complications occur
as the diseases progress, for example, bleeding, perforation, and fistula during this stage.
These terminologies are used interchangeably. But at the same time have different meanings. An article that was in Pubmd central about the diverticular disease stated this as the disease of the Western civilization”. No fiber and high red meat consumption have been correlated to it. However, the real cause of this disease has not been found yet.
Who is at risk for diverticulosis?
It is estimated that half of adults over 60 have developed diverticulosis. It is also more prevalent in ages 65 and older but gets worse as the age progresses to 85 years and over.
According to the National Institute of Health (NIH). Most people with diverticulosis will never have any signs or symptoms. Unless it goes to the next stage where inflammation occurs.
That sets things in the next stage, which is inflammation called diverticulitis.
About 15%-25% of mild to severe symptoms.
As the study suggests less than 5% of individuals will experience diverticulitis. 200, 000 people will end up in the hospital. 71,000 of them are hospitalized for complications in the United States of America every year.
More white Americans are affected than their counterparts. Also, more females seem to be the victims of this disease than men. Black forks are more common to get complications like bleeding due to several factors, for example, health disparities.
The risk factors that contribute to diverticulosis are:

- Obesity – The higher your BMI ( body mass index) the riskier with diverticular disease.
- Low fiber intake- Diet is a big factor, as most people consume refined and low fiber diets, which contributes to constipation
- Smoking – Increases the risk of bowel contraction
- Red meat – Many people consume more red meat.
- Lack of exercise/sedentary lifestyle – Especially vigorous exercise eg running
- NSAIDs ( non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs} increase the risk of complications such as bleeding.
- Age– The older we get the higher the risk
- Gender – Women are more prone to diverticular disease than men as research suggests.
What are the symptoms of diverticulosis?
The most common symptom is pain in the right lower abdomen. But in the rare case, an individual might experience it in the left lower abdomen.
The pain is caused by the irritation of the inflamed pouch. Symptoms are like IBS syndrome why? A person can have diarrhea, constipation, or an extreme alternation between diarrhea/constipation. As you can see the similarity they have can easily be mistaken unless other tests are done.
The symptoms can become worse when diverticulitis occurs.
Severe abdominal cramping, high fever, bleeding, pain, and tenderness on the left lower abdomen the majority of the time. In rare cases, it can appear in the right lower abdomen.
What Are The Complications Of Diverticulitis?
- Fistula – An abnormal passage that leads to leakage of colon content to other organs. This can cause more problems like urinary tract infections. In some rare cases, a fistula develops. This occurs between the large intestine, small intestine, uterus, vagina, and abdominal wall.
- Abscess – It is the formation of pus in the formed sac. Causing infection which sometimes might call for an emergency.
- Peritonitis – An infection occurring in the abdominal wall. Causing perforation of the diverticulum (pouch)
Also, more complications can involve other organs, such as the bladder, uterus, etc. It can even cause narrowing of the large intestine. Preventing stool from going through and causing an obstruction.
How do you reduce the risk of diverticulosis?
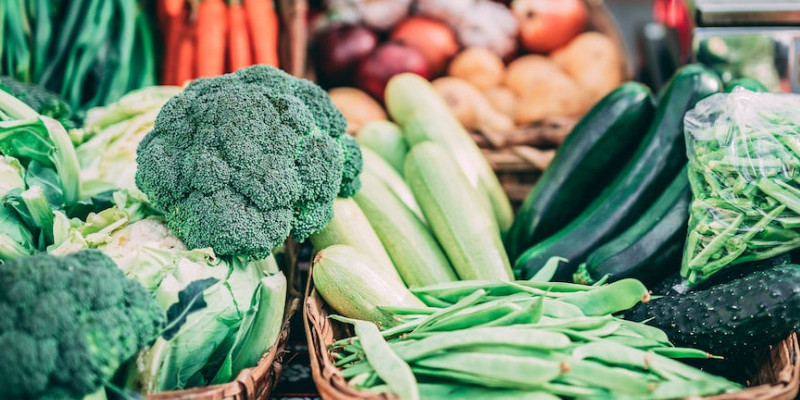

- Increasing high-fiber food intake eg. whole grains, broccoli, green beans,
- Reduction of red meat consumption
- Doing more vigorous exercise
- Losing weight, especially around the belly area
- Reducing or stopping NSAID medication such as Advil, aspirin, etc
- Stop smoking as it affects bowel contraction
How is diverticulosis diagnosed?
Most of the time this disorder is found by accident. While doing tests for other gut conditions or routine procedures such as colonoscopies.
When diverticulitis progresses it becomes symptomatic. Thus people seek out help from their healthcare providers.
Computed tomography (CT )scans or Magnetic renosance imaging ( MRI) of the abdomen and pelvis are some diagnostic tests carried out. And that is how many people found out they have diverticulosis.
What foods should you avoid with diverticulosis?
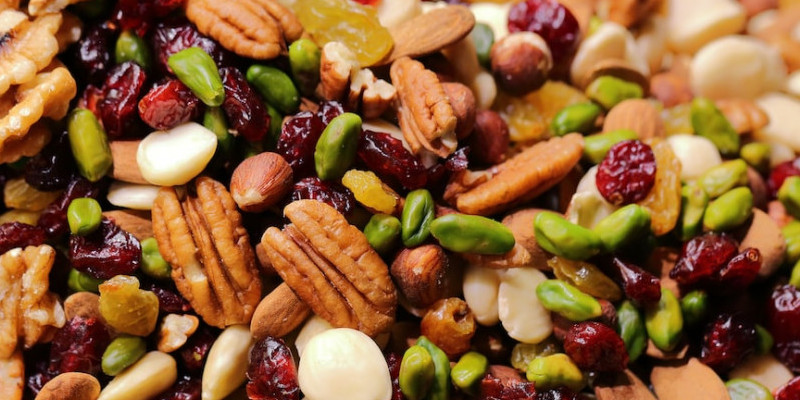

Some of the foods to avoid unnecessary flareup and pain that can land you in the hospital are:
- Popcorn – Can get stuck in the diverticulum and irritate, causing flare-ups leading you to the emergency room.
- Nuts – Also do the same thing as popcorn so its better to avoid it at all cost
- Seeds – Such as corn, fruits, and vegetables like cucumber, zucchini, etc. should be avoided as well since they tend to accumulate in the diverticula and increase symptoms of diverticulitis.
- Fruit and vegetables with skin – Have high fiber that is difficult to digest and should be avoided until your condition gets better.
- Greens – You might say this has fiber why should I void it? only when it is raw, however, boiling it and making it into a puree consistency is recommended. Also starting small amounts is better to prevent any problems.
- Whole grains – Have high fiber making digestion difficult. Especially people with diverticulosis so avoiding these grains is better until the gut heals.
- Spicy foods – It is advisable to avoid spicy foods due to causing gas and pain
- Dairy – Many people have trouble digesting dairy eg Milk, cheese, and the like so eliminating them can ease diverticulosis.
- Bell pepper – This is another food that should be avoided at all costs because of its thick skin. It can a be culprit that can trigger an attack of diverticulitis.
What foods/ supplements help with diverticulitis?
- Bone broth and lots of fluids – Calms down an irritated colon and at the same time nourishes the body.
- Cooked fruits and vegetables – Remove the skin to prevent an attack
- Garlic – As studies suggest garlic is good and benefits the colon because it has antimicrobial properties (natural antibiotic)
- Flaxseeds – Contain high fiber that helps with constipation which is a precursor for diverticulosis. It reduces inflammation of the gut as well
- Probiotics – Help balance the gut microbiome, aid in healing infected diverticula, and prevent recurrent diverticulitis.
- Omega fatty acids – Found in fish and flaxseeds, they prevent inflammation in the colon with the help of a doctor, you can decide if this is good for your condition or if there is any reaction with the medicine you’re taking
Conventional Ways of Treating Diverticulitis
Treatment might depend on the severity of the disease. For example, in mild cases, resting the bowels by consuming a liquid diet and oral antibiotics plan of care. Also over-the-counter pain meds such as Tylenol for a few days while the gut heals are recommended.
In severe cases where there are complications, like bleeding. Abscess and severe pain things can go into another level of treatment. Hospitalization might be necessary.
The patients most likely will be on intravenous antibiotics. pain medications. As well as draining the abscess to prevent the infection. When there is bleeding involved, blood transfusions will deem necessary.
As the disease progresses so are the interventions. Surgery is sometimes unavoidable. to save the patient’s life and prevent things from getting worse.
These might include draining the abscess to bowel resection which removes part of the colon. This even leads to putting a colostomy and can be a temporary means of draining waste to a permanent solution depending on the severity of the case.
What are some natural treatments for diverticulitis?
Diet
Bone Broth
When the first symptom of diverticulitis strikes, it is crucial to rest the gut by not consuming solid food and starting a liquid diet.
Here are the steps
- Stage 1—By consuming liquid food, your gut will start cleaning itself and have less work to do to prevent it from working hard. Therefore, eating/drinking bone broth, vegetable broth, or any kind of broth will calm the digestive tract.
- Stage 2—In this next stage, the gut is much calmer than when we move on to vegetables and fruits that are steamed and then pureed. Continuing with the bone broth will nourish the body.
- Stage 3 – As the gut gets used to stage 2 its okay to add raw vegetables, fruits, and whole grains like quinoa, black/brown rice, and sprouted lentils
- Stage 4—At this stage, you can increase your fiber intake to 25-35 grams as the gut is healing. Then, add vegetables/fruits with thicker skin, such as sweet potatoes, bell peppers, etc., in small amounts to prevent any exacerbation of diverticulitis.
Supplements
Aloe Vera

- Aloe vera – Juice has been used for centuries and is still used to help with digestion relieve pain and calms down an inflamed colon.
- Licorice root – Helps to lower acid to decrease heartburn, help empty the colon, and aid in digestion while lowering cholesterol.
- Digestive enzymes – They help in food digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Probiotics – Increasing good bacteria in the gut and preventing pathogenic microbes
Lifestyle changes

Digestion starts in the mouth. Chewing the food thoroughly makes digestion in the colon much easier. It also increases the absorption of nutrients in the gut to fuel the rest of the body.
Daily vigorous exercises such as running and a high-fiber diet help prevent diverticular disease.
Reducing symptoms and flare-ups. Lowering stress levels, as you know, affects the mind and the body. Applying effective stress techniques will prevent diverticula disease.
Diet, supplements, and lifestyle changes help prevent diverticular disease with no or few side effects. But always consult with your health care provider.
It is imperative to visit your healthcare provider when you see bleeding, blood in the stool, severe pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting.
Fistula, bleeding, abscess, and bowel obstruction are symptoms that need immediate intervention.
Prevention is always the key.
As Benjamin Franklin said, “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure”. So why go through the pain when you can take simple steps in preventing it in the first place?
Constipation plays a big role in the formation of diverticula because of straining. The pressure from straining results in bulging sacs leading to diverticulitis.
Thus, taking fiber and plenty of fluids, especially water, will make your colon appreciate you in the long run.
Here are some key takeaways from this article.
- The risk of diverticulosis/diverticulitis increases with age. Another risk factor that makes you susceptible to these disorders is gender. More women than men are prone to it. Obesity plays a role in most diseases, including diverticulitis. Smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, and eating processed food, red meat, and a very low-fiber diet increase the risk.
- Treatments depend on the stage of the disease; the more advanced it is, the more invasive intervention it needs. The most common treatment method starts with resting the bowel by putting patients on a liquid diet and increasing fiber intake. It then includes antibiotics, pain medicine, draining abscessed diverticula, and surgery if necessary for severe situations.
- On the other hand, the natural approach includes resting the bowels by consuming bone broth at the beginning stage. Small steps in fiber include initially steaming and boiling to make them less sensitive to the gut. Eating raw high-fiber fiber is the next step once puree fiber is tolerated. Supplements, probiotics, weight loss, not smoking, and vigorous exercise are very important to the healing of diverticulitis.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2780060/
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/diverticulosis-diverticulitis/definition-facts#complications
- https://badgut.org/information-centre/a-z-digestive-topics/diverticular-disease/
- https://www.pulseandremedy.com/aloe#:~:text=It is a powerful healing,comfort you while providing energy.
- https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/quick-facts-digestive-disorders/diverticular-disease/diverticulosis
- Elizabeth Lipsk. Digestive Wellness 5th Edition. Strengthen the Immune System and Prevent Disease Through Healthy Digestion 2020 (332-334)
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18728264/
- Prospective study of physical activity and the risk of symptomatic diverticular disease in men. – PMC (nih.gov)
- https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/understanding-diverticulitis-symptoms
